Multifocal Pneumonia Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

Multifocal Pneumonia is a less popular respiratory issue with a complex nature and various side effects. Not at all like average pneumonia, which typically influences one region of the lungs, It can include different districts, making it difficult to analyze and treat.
Understanding this condition is indispensable for respiratory health, as it presents interesting difficulties for patients. In this article, we’ll separate multifocal pneumonia from its side effects and find accessible treatment choices.
Main Causes of Multifocal Pneumonia
It comes from different microorganisms, including both bacterial and viral. Understanding the different types of microorganisms responsible for this condition is effective in successfully managing and treating it. These include:
1. Streptococcus:
This bacterium is a major cause of multifocal pneumonia. It regularly spreads through respiratory drops. This includes many diseases for example fever, and chest pain.
2. Legionella:
This bacterium responsible for illness, can lead to extreme pneumonia. Transmission happens through inward breaths of sullied water drops, especially from sources like cooling frameworks, hot tubs, and drinking fountains.
3. Mycoplasma Pneumonia:
This bacterium is a typical reason for abnormal pneumonia, described by milder side effects contrasted with commonplace bacterial pneumonia. Mycoplasma pneumonia spreads through respiratory emissions and is frequently connected with outbreaks in jam-packed settings like schools and military sleeping quarters.
4. Staphylococcus aureus:
While usually found on the skin and mucous layers, certain kinds of Staphylococcus aureus can cause pneumonia, particularly in people with debilitated resistant frameworks or hidden lung conditions. Transmission can happen through direct contact or inward breath of respiratory beads.
5. Flu Infection:
Flu infections, especially flu A and B, are infamous for causing occasional flare-ups of respiratory sickness, including pneumonia. These infections spread through respiratory drops and can prompt serious confusion, particularly in weak populations.
6. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV):
RSV essentially influences infants and small kids, causing respiratory plot diseases going from gentle cold-like side effects to extreme pneumonia. Transmission happens through direct contact with respiratory emissions.
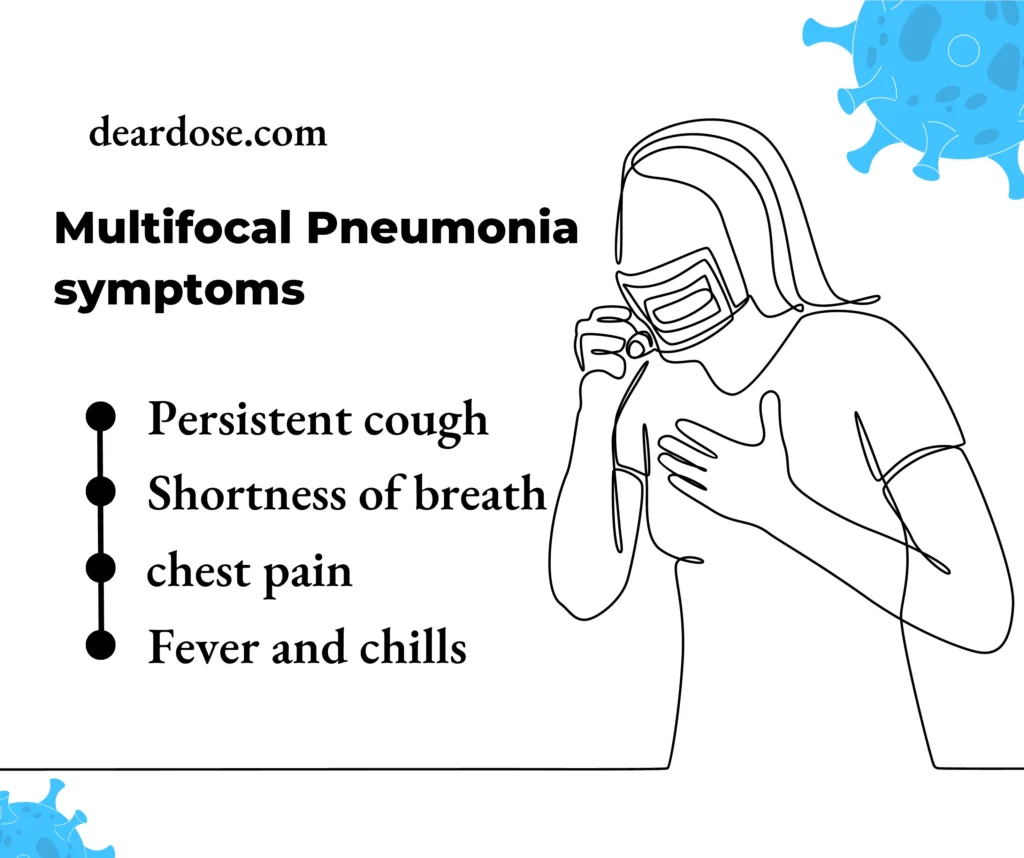
Multifocal Pneumonia Symptoms
It appears through a scope of side effects, frequently covered with pneumonia however recognized by its two-sided contribution. Here are the key signs of central pneumonia to look for:
- Persistent Cough: A sign of multifocal pneumonia, joined by yellow or greenish sputum. It deteriorates with time and may intensify during deep breathing or activity.
- Shortness of breath: It is very normal because of compromised lung capability. People might feel winded, particularly during effort or while lying level.
- Chest Pain: Predominant side effect described as sharp or cutting, deteriorating with hacking or profound relaxing. It might be confined to one or two sides of the chest.
- Fever and Chills: Fever, frequently with chills or afflictions, is a typical fundamental reaction to disease.
- Fatigue: General tiredness and discomfort as the body battles contamination, prompting decreased energy levels and lessened capacity to perform day-to-day exercises.
- Cyanosis: In extreme cases, somewhat blue staining of the skin, lips, or nail beds because of deficient oxygenation, showing critical respiratory trade-off requiring quick clinical consideration.
- Different Side effects: Quick breathing, fast pulse, loss of hunger, sickness, and disarray, particularly in more established people or those with hidden medical issues.
How is Multifocal Pneumonia Identified?
Radiological imaging assumes an essential part in diagnosing this pneumonia and recognizing it from other respiratory circumstances. Normal findings include:
- Consolidations: Areas of lung tissue that seem thick and misty on imaging, showing the presence of liquid or inflammatory material.
- Infiltrates: Inconsistent areas of expanded lung thickness, suggestion of irritation or infection.
- Pleural Emissions: Gatherings of liquid in the pleural depression, frequently found in additional extreme instances of pneumonia.
- Ground-Glass Opacities: Dim areas of expanded lung thickness, demonstrating incomplete filling of airspaces with liquid or incendiary cells.
Treatment for multifocal Pneumonia
Depending upon the seriousness of the disease, as well as the reason for pneumonia, the treatment plan can vary enormously. Firstly, for treatment to happen, a proper finding should be made to decide the seriousness and the reason for the infection.
Diagnosing pneumonia can be achieved through different strategies, for example, a chest X-beam, blood test, sputum culture, beat oximetry, chest CT filter, bronchoscopy, or a pleural liquid culture.
For a great many people who show gentle side effects, treatment will spin around home rest and hydration, with a suitable prescription recommended.
If the pneumonia is bacterial, anti-infection agents will be recommended. If the infection is viral, a few antiviral prescriptions might be recommended, like Tamiflu. Concerning parasitic pneumonia, antifungal drugs will be used to clear the contamination.
Vaccines that protect against normal microorganisms that cause pneumonia, similar to Streptococcus pneumonia and flu, can make diseases less inclined to occur and less serious assuming they do. This is particularly significant for individuals with other medical problems, more seasoned grown-ups, small children, and individuals whose immune systems also don’t work properly.
Risk factors
Pneumonia has a few risk factors, the fundamental ones being the following:
- Infancy
- Smoking
- Alcoholism
- Immunosuppressive circumstances
- Cardiovascular illnesses
- Cerebrovascular illnesses
- Renal illnesses
- Liver infections
- Dementia
- Diabetes
Conclusion
It is a complex respiratory issue with different side effects and complex indicative contemplations. It requires a careful methodology that thinks about every patient’s interesting circumstance, from recognizing various microorganisms to figuring out different possible diagnoses.
At UCF Health, we’re focused on giving first-rate care and backing to people managing pneumonia.